Get the latest updates From BL Soni College Bhilwara
What is the difference between CMYK and RGB color modes in graphic design?
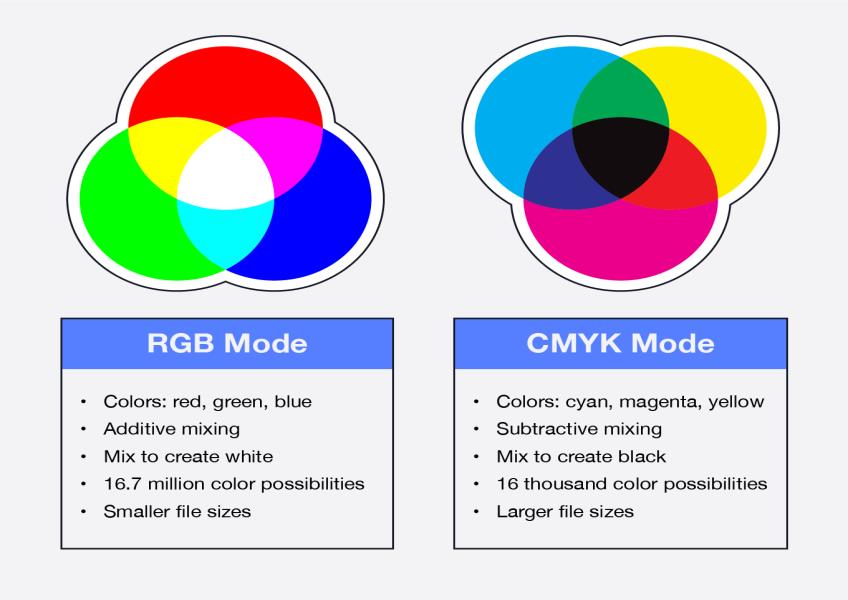
CMYK and RGB are two different color modes used in graphic design, and they serve different purposes because they are optimized for different mediums: print and digital screens, respectively. Here's an explanation of the key differences between CMYK and RGB color modes: CMYK (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Key/Black): Purpose: CMYK is primarily used for print media, such as magazines, brochures, posters, and packaging. It's the standard color mode for most commercial printing processes. Color Model: CMYK is a subtractive color model, meaning it starts with white (or the color of the paper) and subtracts color to create the final image. By mixing varying percentages of cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks, a wide range of colors can be produced. Color Range: CMYK has a more limited color gamut compared to RGB. This means it can reproduce fewer colors, especially in the bright and vibrant range. Some colors that can be displayed on screens may not be achievable in CMYK printing. Color Profiles: Printers often use specific CMYK color profiles to ensure color accuracy. Designers need to be aware of these profiles when preparing files for print. Color Matching: Achieving exact color matches in CMYK can be challenging, as it depends on the printer, ink quality, and paper used. Designers may need to make adjustments to ensure color consistency. RGB (Red, Green, Blue): Purpose: RGB is used for digital media, including computer monitors, television screens, digital cameras, and web design. It's the standard color mode for anything that emits light. Color Model: RGB is an additive color model, which means it starts with black (no light) and adds red, green, and blue light to create colors. When fully combined, these colors produce white light. Color Range: RGB has a broader and more vibrant color gamut compared to CMYK. It can display many colors that are outside the range of CMYK, making it suitable for highly saturated and vivid visuals. Color Consistency: RGB colors are generally consistent across different devices with standard color profiles, such as sRGB. However, slight variations can still occur between screens. Web and Digital Design: RGB is the preferred color mode for designing websites, digital graphics, video content, and any visuals intended for electronic screens. In summary, the key difference between CMYK and RGB color modes lies in their purpose and color models. CMYK is used for print, employs a subtractive color model, and is more limited in its color range. RGB is used for digital screens, employs an additive color model, and offers a wider color gamut. When working on design projects, it's important to choose the appropriate color mode based on the intended medium to ensure accurate and consistent color reproduction.