Get the latest updates From BL Soni College Bhilwara
How can graphic design be used to enhance user experience (UX)
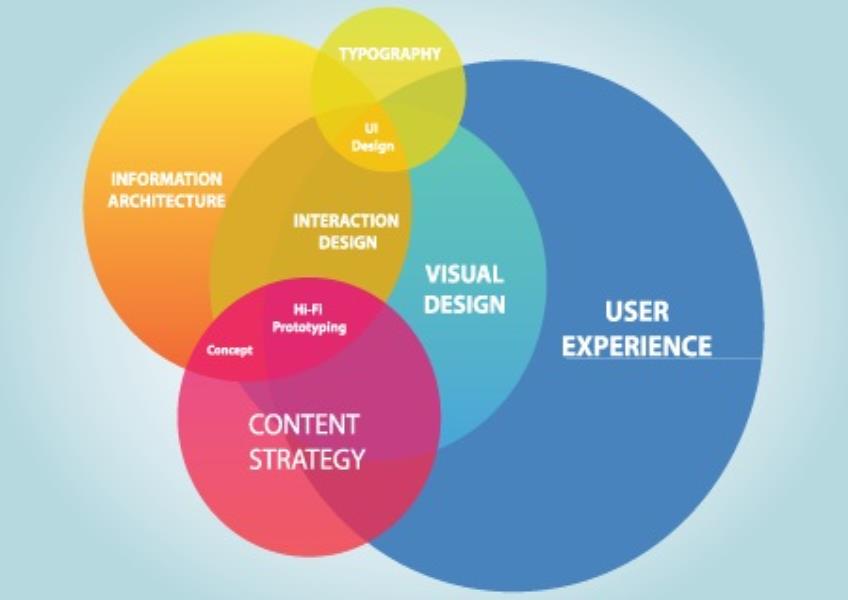
Graphic design plays a crucial role in enhancing user experience (UX) across various digital and physical platforms. Effective graphic design can make information more accessible, improve aesthetics, and create a positive emotional connection with users. Here are ways in which graphic design can enhance UX: Clarity and Readability: Typography: Choosing the right fonts and text sizes ensures that content is legible and easy to read. Consistent typography also helps establish a visual hierarchy. Whitespace: Proper use of whitespace (margins, padding, line spacing) helps reduce visual clutter and improves content comprehension. Color Contrast: High contrast between text and background colors improves readability, especially for users with visual impairments. Navigation and Information Architecture: Iconography: Well-designed icons can quickly convey meaning and aid in navigation, making it easier for users to understand the interface. Menu Design: Thoughtful menu layouts and navigation elements make it intuitive for users to find what they need. Information Hierarchy: Clear visual cues such as headings, subheadings, and use of color help users understand the structure of content. Branding and Consistency: Visual Identity: Consistent use of branding elements (logo, colors, typography) creates a cohesive and recognizable brand identity. UI Elements: Consistency in the design of buttons, forms, and other UI elements across the platform helps users navigate with confidence. Visual Appeal: Aesthetics: Attractive and visually pleasing design elements can positively influence user perception and engagement. Images and Graphics: High-quality images and graphics can enhance storytelling and provide context to content. Animation: Thoughtful use of animations can guide users' attention and create a dynamic and engaging experience. Responsiveness: Adaptive Design: Ensuring that graphic elements adapt to various screen sizes and orientations improves usability on different devices. Performance: Optimizing graphic assets for quick loading times prevents frustration due to slow website or app performance. Feedback and Interaction: Feedback Elements: Visual cues (e.g., hover effects, button states) inform users about the outcome of their actions, helping them understand how the interface works. Microinteractions: Small, subtle animations or visual changes in response to user actions can enhance the sense of interactivity and provide feedback. Accessibility: Alt Text: Providing descriptive alt text for images and graphics helps users with disabilities access content. Color Accessibility: Ensuring that color choices meet accessibility standards benefits users with color vision deficiencies. User Engagement: Call to Action (CTA): Well-designed CTAs encourage user interaction and guide them toward desired actions (e.g., sign-up, purchase). Visual Storytelling: Graphics and images can be used to tell a story or convey information in a compelling way. User-Centered Design: User Testing: Involving users in design testing and feedback sessions helps identify design issues and improve the UX based on real user input. Loading and Progress Indicators: Loading Screens: Providing engaging loading animations or graphics can make wait times feel shorter and less frustrating for users. Progress Bars: Indicating progress during lengthy processes (e.g., file uploads) keeps users informed and patient. Graphic design is an integral part of UX design, working in tandem with other aspects like usability, content strategy, and interaction design to create a seamless and enjoyable user experience. It should be user-focused, aiming to make information accessible, interactions intuitive, and the overall experience visually appealing and engaging.