Get the latest updates From BL Soni College Bhilwara
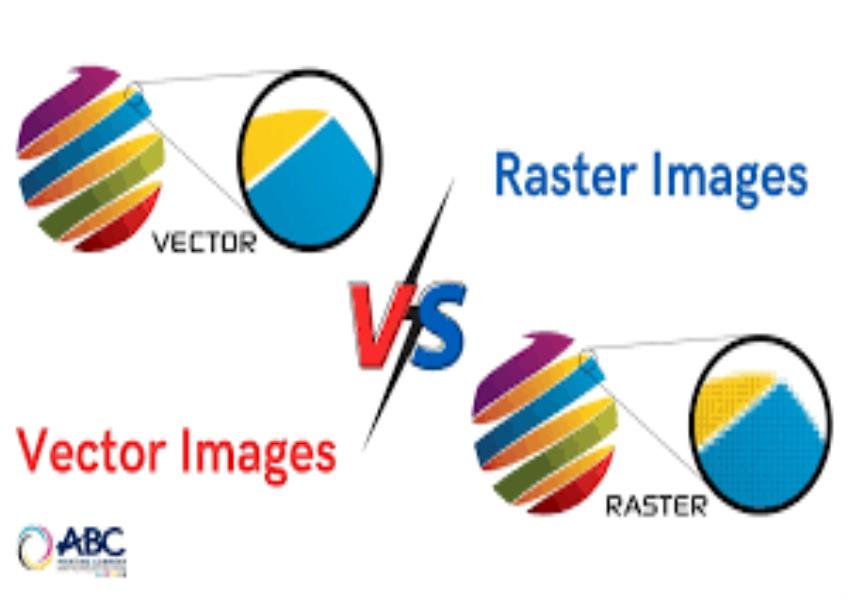
What is the difference between raster and vector graphics?
Raster and vector graphics are two primary types of digital image formats, and they differ in how they represent and store visual information: Raster Graphics (Bitmap Images): Representation: Raster graphics are composed of a grid of individual pixels (picture elements). Each pixel contains a specific color value, and together, they form the image. Resolution: Raster images have a fixed resolution, typically measured in dots per inch (DPI) or pixels per inch (PPI). When you resize a raster image, you either stretch the pixels (resulting in loss of quality) or reduce the image's size (resulting in loss of detail). Scalability: Raster images are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality and become pixelated when scaled up. Enlarging a small raster image often results in a blurry or jagged appearance. File Types: Common file formats for raster graphics include JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP, and TIFF. Vector Graphics: Representation: Vector graphics use mathematical formulas (vectors) to describe shapes and lines. Instead of pixels, they are composed of paths, curves, and geometric objects defined by their attributes (such as coordinates, colors, and stroke widths). Resolution: Vector graphics are resolution-independent. They can be scaled up or down without any loss of quality or detail because the shapes and lines are recalculated based on the new size. Scalability: Vector graphics are ideal for designs that need to maintain sharpness and clarity at various sizes, such as logos and illustrations. File Types: Common file formats for vector graphics include SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics), AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS (Encapsulated PostScript), and PDF (Portable Document Format, which can contain both raster and vector elements). Key Differences: Scalability: This is the most significant difference. Raster images lose quality when scaled up, while vector images maintain their quality and sharpness at any size. Resolution: Raster images have a fixed resolution, while vector images are resolution-independent. Editing: Vector graphics are more suitable for precise editing and manipulation because they consist of editable mathematical objects. Raster images are more challenging to edit without some loss of quality. File Size: Raster images tend to have larger file sizes, especially at high resolutions, whereas vector files are generally smaller. Use Cases: Raster images are often used for photographs, digital paintings, and detailed images with complex shading. Vector graphics are used for logos, icons, typography, and illustrations where scalability and precision are essential. The choice between raster and vector graphics depends on the specific requirements of your project. For photographs and images with continuous tones and complex details, raster graphics are appropriate. For designs requiring scalability, precision, and the ability to easily edit and adapt shapes and lines, vector graphics are the better choice.